- Category: Reporting and disclosure
- Industry: Consulting
Why Physical Climate Risks and Value Chain Risk Matter for CSRD Reporting
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) applies to approximately 50’000 companies within the European Union and also to certain companies abroad that are indirectly affected. While CSRD defines which companies are affected, the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) provides the details on how companies must disclose sustainability-related matters.
ESRS provides requirements for different environmental areas, namely climate change, pollution, water and marine resources, biodiversity and ecosystems, resource use, and circular economy. In the following, we will focus on ESRS E1 (Climate Change).
To ensure international alignment, ESRS is structured similarly to ISSB Standards, which integrated TCFD recommendations. This is reflected by focusing on four main pillars of an organization or undertaking that is subject to CSRD disclosures: Governance, Strategy, Impact, risk and opportunity management, and Metrics and Targets.
- Governance
- Strategy
- Impact, risk, and Opportunity Managements
- Metrics and Targets
One of the key requirements related to physical climate risks is that companies need to disclose the process of identifying and assessing material climate-related impacts, risks, and opportunities (IRO) related to climate-related physical risks (ESRS E1 – 20 b) in their own operations and along the upstream and downstream value chain:


In the identification of physical climate hazards,
- at least one high-emission climate scenario needs to be used, and
- the assessment needs to analyze how assets and business activities may be exposed to climate-related hazards.
In a first step, the analysis needs to assess the gross physical risk, i.e. before any mitigation or resilience measures.
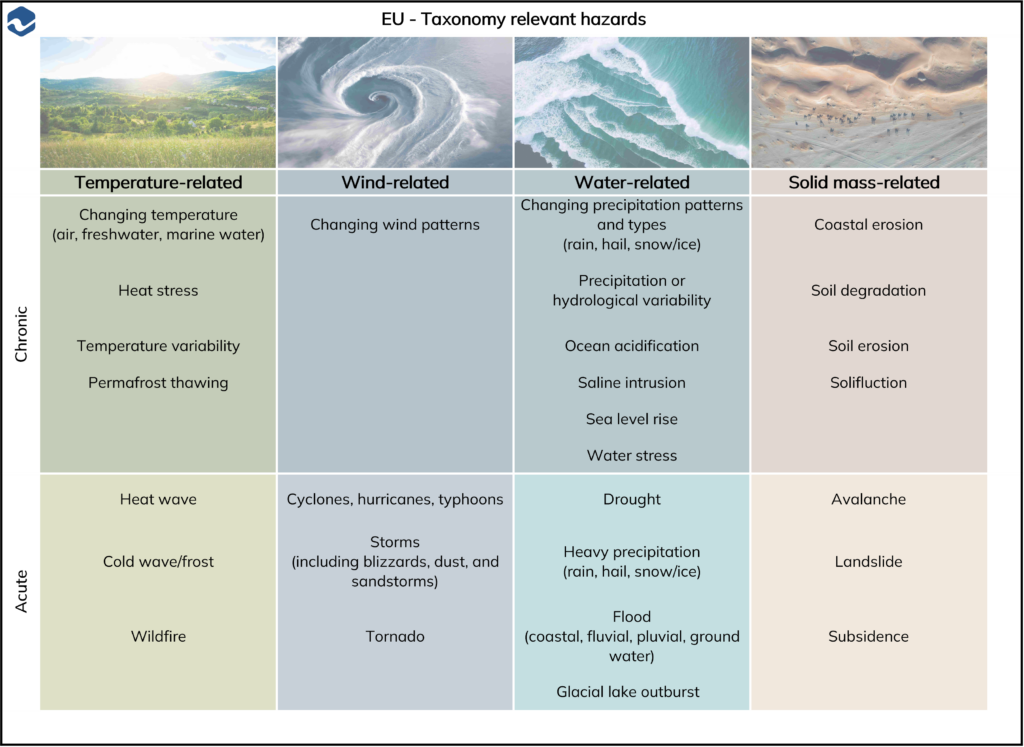
The Application Requirement ESRS E1 AR 11 prescribes that when identifying climate-related hazards, companies need to explain whether and how they assessed the hazards from the list below and how business activities might be affected by these hazards:
| EU – Taxonomy relevant hazard | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic | Temperature-related | Wind-related | Water-related | Solid mass-related |
 |  |  |  | |
| Changing temperature (air, freshwater, marine water) | Changing wind patterns | Changing precipitation patterns and types (rain, hail, snow/ice) | Coastal erosion | |
| Heat stress | Precipitation or hydrological variability | Soil degradation | ||
| Temperature variability | Ocean acidification | Soil erosion | ||
| Permafrost thawing | Saline intrusion | Solifluction | ||
| Sea level rise | ||||
| Water stress | ||||
| Acute | Heat wave | Cyclones, hurricanes, typhoons | Drought | Avalanche |
| Cold wave / front | Storms (including blizzards, dust, and sandstorms | Heavy precipitation (rain, hail, snow/ice) | Landslide | |
| Wildfire | Tornado | Flood (coastal, fluvial, pluvial, ground water) | Subsidence | |
| Glacial lake outburst | ||||
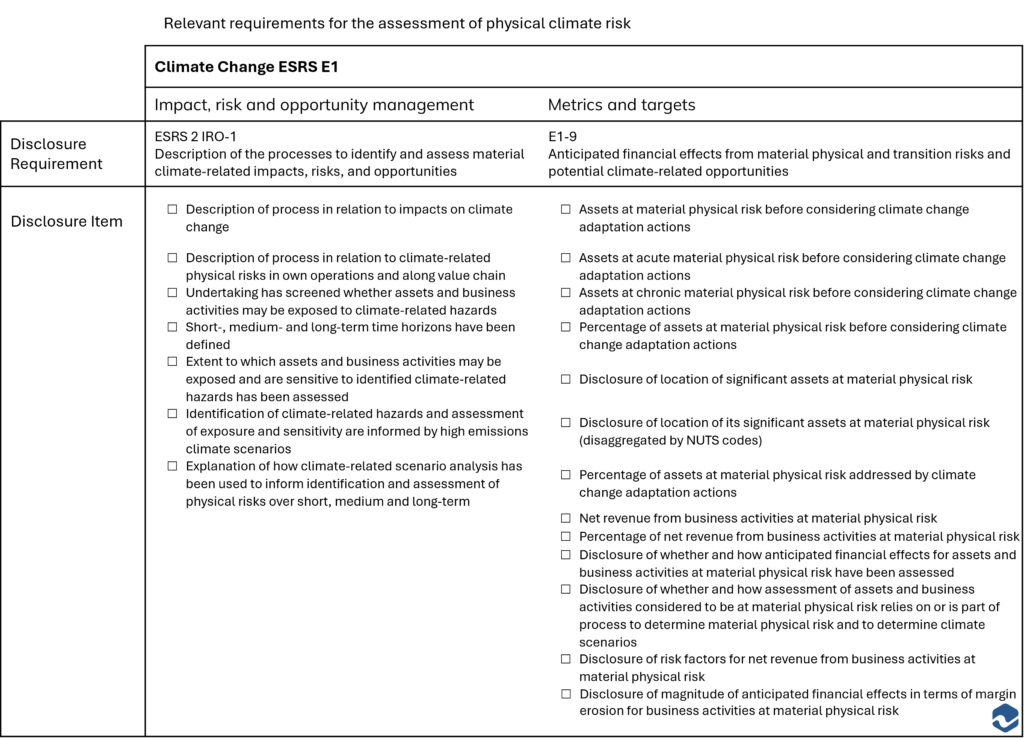
The European Financial Reporting Advisory Group (EFRAG) recently published a set of guidelines and a list of ESRS data points. In particular, the following reporting requirements are relevant for the assessment of physical climate risks:
Relevant requirements for the assessment of physical climate risk
| Climate Change ESRS E1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impact, risk and opportunity management | Metrics and targets | |||
| Disclosure Requirement | ESRS 2 IRO-1 Description of the processes to identify and assess material climate-related impacts, risks, and opportunities | E1-9 Anticipated financial effects from material physical and transition risks and potential climate-related opportunities | ||
| Disclosure Item |
|
|
||
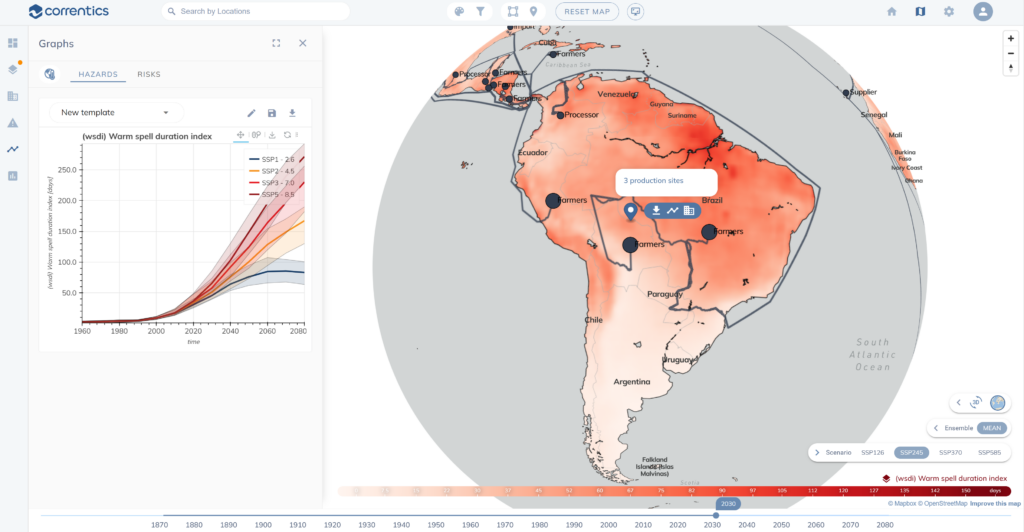
How Correntics can support:
Correntics has developed a sophisticated software solution to efficiently assess physical climate risks under different future scenarios. The solution is used by corporations and consulting firms to speed up the process of assessing the materiality, impacts, risks, and opportunities, based on the latest scientific data. Do you want to learn more about how we can support you?